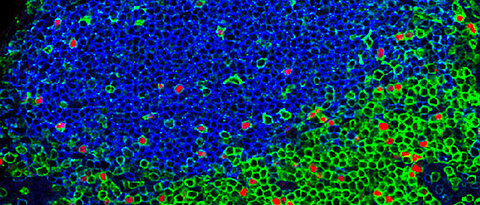
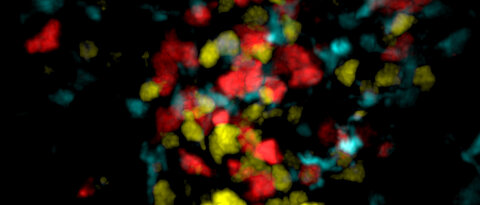
Tissue-resident Lymphocytes (Gasteiger Lab)
Das Immunsystem „zu Gast“ in verschiedensten Organen: Entstehung und Funktionen von gewebe-residenten Lymphozyten
Fast alle Organe und anatomischen Kompartimente „beherbergen“ gewebe-residente Lymphozyten, welche dort lokale Netzwerke ausbilden. So sind diese Zellen zum Beispiel in verschiedensten Barriereorganen wie der Haut, der Lunge und dem Darm strategisch positioniert um die Immunüberwachung und die Abwehr von Mikroben an vorderster Front zu unterstützen. Zusätzlich zu unmittelbaren immunologischen Effektorfunktionen interagieren diese Lymphozyten mit hämatopoetischen und nicht-hämatopoetischen Zellen vor Ort und tragen so zu den physiologischen Mechanismen der Gewebehomöostase, -reparatur und -barrierefunktion bei. Die erst kürzlich entdeckten innaten lymphoiden Zellen (ILCs) scheinen sich als Teil ihrer "standardmäßigen" Entwicklung während der Ontogenese in verschiedenste Organe zu integrieren. Gewebsresidente T-Zellen hingegen können als spezialisierte Gedächtniszellen durch Infektionen oder Impfungen entstehen und dann, nach der Abheilung, vor allem in betroffenen Organen verbleiben. Unter physiologischen Bedingungen unterscheiden sich die mikroanatomischen Nichen, die Anzahl und Zelltypen in den lokalen Lymphozytennetzwerken sehr stark zwischen den verschiedenen Organen. Wissenschaftler des Instituts für Systemimmunologie erforschen, wie und wo genau sich lokale Lymphozyten-Netzwerke in den verschiedenen Geweben bilden und positionieren und welche organspezifische Funktionen sie übernehmen. Die Wissenschaftler untersuchen außerdem, mit welchen anderen Zellen des Immunsystems die lokalen Abwehrzellen interagieren, wenn es zum Beispiel während einer Infektion zur Rekrutierung von anderen Immmunzellen aus dem Blut kommt. Durch die Aufklärung der Wechselwirkungen und Funktionen dieser Zellen versuchen sie zu verstehen, wie gewebe-residente Lymphozyten zur balancierten Organfunktion, zur Immunabwehr oder aber auch zu Erkrankungen wie Entzündungen und Tumore beitragen, und wie diese Erkenntnisse Patienten helfen können.
Weitere Informationen finden Sie auf der englischen Seite und hier.
Local networks of tissue-resident lymphocytes are strategically positioned in most anatomical compartments, including epithelial barrier surfaces such as the skin, the lung and the gut, where they provide immune surveillance and front-line defense to microbial invasion. In addition to immediate immunological effector activities, tissue-resident lymphocytes interact with both hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells and contribute to physiologic mechanisms of tissue homeostasis, repair and barrier function. The recently discovered innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) and tissue-resident memory T cells represent populations of prototypic lymphocytes that appear to adopt the fate of tissue-residency either “by default” during ontogeny, or, “as a result of induction” during peripheral differentiation, respectively. Under physiologic conditions, the size, microanatomical localization and subset composition of the local pools of lymphocytes differs quite dramatically among different organs, but the mechanisms that instruct cell-intrinsic adaptations and the development, maintenance and coordinated function of resident lymphocytes in specific tissue environments are poorly understood.
Innate Lymphoid Cells (ILCs): Our previous work revealed that the currently known subsets of ILCs are locally maintained as tissue-resident cells in all examined lymphoid and non-lymphoid organs (Gasteiger et al., Science 2015). The notion that ILCs form an integral part of their “host”-tissue suggests the presence of mechanisms of local development, differentiation and maintenance, as well as tissue-specific imprinting and specialization of ILCs.
Tissue-resident memory T (TRM) cells: We have recently identified antigen-dependent, “APC-proximal” competition of CD8+ T cells in non-lymphoid tissues as a mechanism that regulates the generation of local pools of memory T cells (Muschaweckh et al., J Exp Med 2016). These findings highlight local mechanisms for the “selection” or fine-tuning of a regional repertoire of resident memory cells that can optimally recognize and hence anticipate those antigens being present (and eventually presented) in the respective tissue, or, as suggested by our work, respective tissue regions. Such mechanisms may be critical to adapt the local pools of tissue-resident memory T (TRM) cells in response to regionally persisting pathogens, or to enable the local anticipation of tissue-invasion by regionally distinct microbial communities.
These complementary lines of research should enable us to delineate the nature of shared and cell-type specific characteristics of tissue-resident innate versus adaptive lymphocytes. In our quest to understand the development and maintenance of the “functional architecture” of local networks of tissue-lymphocytes, we are employing genetic mouse models, experimental models of inflammatory diseases, tumors and infection, single cell genomics and advanced imaging. We expect that our studies will contribute to a better understanding of the role of tissue-specific immunity in the regulation of immune homeostasis and defense.
Innate lymphocytes, including natural killer cells (NK) and recently discovered novel subsets of innate lymphoid cells (ILC) exert key functions in coordinating local immune responses, including the killing of infected cells, the production of hallmark cytokines that orchestrate immune responses, and the secretion of tissue-protective factors. Innate lymphocytes respond rapidly to environmental cues without the need for further differentiation. The ease of activation needs to be balanced by stringent control mechanisms because excessive activation of innate lymphocytes contributes to a loss of tissue function and facilitates inflammatory processes as well as the exacerbation of infection-associated pathologies.
The cellular interactions and the molecular mechanisms governing the regulation and activation of innate lymphocytes are therefore highly relevant for a broad range of physiologic and pathologic immune responses. Current research has largely focused on the role of innate cytokines and alarmins for the homeostasis and function of innate lymphocytes. In addition to their innate effector functions, ILC and NK cells have been found to participate in shaping and regulating adaptive immune responses. Whether the adaptive immune system may in turn contribute to the control of innate lymphocyte function and homeostasis is largely unknown. During our recent work, we have identified novel regulatory interactions between cells of the adaptive immune system and innate lymphocytes mediated by the “adaptive” cytokine IL-2. Our goal is now to determine the cellular mechanisms and the physiological relevance of these interactions using clinically relevant disease models. We are investigating additional pathways through which adaptive and innate lymphocytes may interact, as well as their potential therapeutic implications. Our aim is to understand the context-dependent physiological and pathological functions of innate lymphocytes for immune homeostasis as well as infectious and inflammatory diseases.
Gasteiger link pubmed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Selected Articles
-
A distinct priming phase regulates CD8 T cell immunity by orchestrating paracrine IL-2 signals. Katarzyna Jobin, Deeksha Seetharama, Lennart Rüttger, Cloe Fenton, Ekaterina Kharybina, Annerose Wirsching, Anfei Huang, Konrad Knöpper, Tsuneyasu Kaisho, Dirk H. Busch, Martin Vaeth, Antoine Emmanuel Saliba, Frederik Graw, Alain Pulfer, Santiago F. Gonzalez, Dietmar Zehn, Yinming Liang, Milas Ugur, Georg Gasteiger and Wolfgang Kastenmüller. Science 388,eadq1405(2025).DOI:10.1126/science.adq1405
-
Circulating NK cells establish tissue residency upon acute infection of skin and mediate accelerated effector responses to secondary infection. Tommaso Torcellan, Christin Friedrich, Rémi Doucet-Ladevèze, Thomas Ossner, Virgínia Visaconill Solé, Sofie Riedmann, Milas Ugur, Fabian Imdahl, Stephan P. Rosshart, Sebastian J. Arnold, Mercedes Gomez de Agüero, Nicola Gagliani, Richard A. Flavell, Simone Backes, Wolfgang Kastenmüller, Georg Gasteiger. Immunity. 2024 Jan 9; 57(1):124-140.e7. ; doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2023.11.018. Epub 2023 Dec 28.
-
Lymphatic migration of unconventional T cells promotes site-specific immunity in distinct lymph nodes. Marco A. Ataide, Konrad Knöpper, Paulina Cruz de Casas, Milas Ugur, Sarah Eickhoff, Mangge Zou, Haroon Shaikh, Apurwa Trivedi, Anika Grafen, Tao Yang, Immo Prinz, Knut Ohlsen, Mercedes Gomez de Agüero, Andreas Beilhack, Jochen Huehn, Mauro Gaya, Antoine-Emmanuel Saliba, Georg Gasteiger, Wolfgang Kastenmüller. Immunity. 2022 Oct 11; 1813-1828.e9. ; doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.07.019. Epub 2022 Aug 23.
-
Novel antigen-presenting cell imparts T(reg)-dependent tolerance to gut microbiota. Blossom Akagbosu, Zakieh Tayyebi, Gayathri Shibu, Yoselin A. Paucar Iza, Deeksha Deep, Yollanda Franco Parisotto, Logan Fisher, H. Amalia Pasolli, Valentin Thevin, Rasa Elmentaite, Maximilian Knott, Saskia Hemmers, Lorenz Jahn, Christin Friedrich, Jacob Verter, Zhong-Min Wang, Marcel van den Brink, Georg Gasteiger, Thomas G. P. Grünewald, Julien C. Marie, Christina Leslie, Alexander Y. Rudensky, Chrysothemis C. Brown. Nature. 2022 Sep 07; 610, 752–760 (2022). ; doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05309-5. Epub 2022 Sep 7.
-
Embryonic and neonatal waves generate distinct populations of hepatic ILC1s. Colin Sparano, Darío Solís-Sayago, Anjali Vijaykumar, Chiara Rickenbach, Marijne Vermeer, Florian Ingelfinger, Gioana Litscher, André Fonseca, Caroline Mussak, Maud Mayoux, Christin Friedrich, César Nombela-Arrieta, Georg Gasteiger, Burkhard Becher, Sonia Tugues. Sci Immunol. 2022 Sep 02; 7(75):eabo6641 ; doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abo6641
-
Type 1 conventional dendritic cells maintain and guide the differentiation of precursors of exhausted T cells in distinct cellular niches. Sabrina Dähling, Ana Maria Mansilla, Konrad Knöpper, Anika Grafen, Daniel T Utzschneider, Milas Ugur, Paul G Whitney, Annabell Bachem, Panagiota Arampatzi, Fabian Imdahl, Tsuneyasu Kaisho, Dietmar Zehn, Frederick Klauschen, Natalio Garbi , Axel Kallies, Antoine-Emmanuel Saliba, Georg Gasteiger, Sammy Bedoui, Wolfgang Kastenmüller. Immunity. 2022 Mar 30; S1074-7613(22)00129-7. ; doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.03.006
-
Effector differentiation downstream of lineage commitment in ILC1s is driven by Hobit across tissues. Friedrich, C., Taggenbrock, R.L.R.E., Doucet-Ladevèze, R. et al. Effector differentiation downstream of lineage commitment in ILC1s is driven by Hobit across tissues. Nat Immunol. 2021 Aug. 30. doi:10.1038/s41590-021-01013-0 open access Interactive online resource/Interactive atlas of liver ILC1
-
Skin-resident innate lymphoid cells converge on a pathogenic effector state. Bielecki P, Riesenfeld SJ, Hütter JC, Torlai Triglia E, Kowalczyk MS, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Lian M, Amezcua Vesely MC, Kroehling L, Xu H, Slyper M, Muus C, Ludwig LS, Christian E, Tao L, Kedaigle AJ, Steach HR, York AG, Skadow MH, Yaghoubi P, Dionne D, Jarret A, McGee HM, Porter CBM, Licona-Limón P, Bailis W, Jackson R, Gagliani N, Gasteiger G, Locksley RM, Regev A, Flavell RA. Nature. 2021 Feb 3. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03188-w. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33536623.
-
Fate mapping of single NK cells identifies a type 1 innate lymphoid-like lineage that bridges innate and adaptive recognition of viral infection. Sophie Flommersfeld, Jan P. Böttcher, Jonatan Ersching, Michael Flossdorf, Philippa Meiser, Ludwig O. Pachmayr, Justin Leube, Inge Hensel, Sebastian Jarosch, Qin Zhang, M. Zeeshan Chaudhry, Immanuel Andrae, Matthias Schiemann, Dirk.H. Busch, Luka Cicin-Sain, Joseph C. Sun, Georg Gasteiger, Gabriel D. Victora, Thomas Höfer, Veit R. Buchholz, Simon Grassmann. Immunity. 2021 Oct 12; 54(10):2288-2304.e7. ; doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.08.002
-
Divergent Role for STAT5 in the Adaptive Responses of Natural Killer Cells. Wiedemann GM, Grassmann S, Lau CM, Rapp M, Villarino AV, Friedrich C, Gasteiger G, O'Shea JJ, Sun JC. Cell Rep. 2020 Dec 15;33(11):108498. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108498. PMID: 33326784; PMCID: PMC7773031.
-
BATF3 programs CD8+ T cell memory. Ataide MA, Komander K, Knöpper K, Peters AE, Wu H, Eickhoff S, Gogishvili T, Weber J, Grafen A, Kallies A, Garbi N, Einsele H, Hudecek M, Gasteiger G, Hölzel M, Vaeth M, Kastenmüller W. Nat Immunol. 2020 Nov;21(11):1397-1407. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0786-2.
-
In Situ Maturation and Tissue Adaptation of Type 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Progenitors Zeis P, Lian M, Fan X, Herman JS, Hernandez DC, Gentek R, Elias S, Symowski C, Knöpper K, Peltokangas N, Friedrich C, Doucet-Ladeveze R, Kabat AM, Locksley RM, Voehringer D, Bajenoff M, Rudensky AY, Romagnani C, Grün D, Gasteiger G. Immunity. 2020 Oct 13;53(4):775-792.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.09.002 Zeis, Lian, et al..pdf Interactive online resource: ILC2 Atlas
-
Bacterial coinfection restrains antiviral CD8 T-cell response via LPS-induced inhibitory NK cells. Straub T, Freudenberg MA, Schleicher U, Bogdan C, Gasteiger G, Pircher H. Nat Commun. 2018 Oct 8;9(1):4117. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06609-z
-
Antigen-dependent competition shapes the local repertoire of tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells. Muschaweckh A, Buchholz VR, Fellenzer A, Hessel C, König PA, Tao S, Tao R, Heikenwälder M, Busch DH, Korn T, Kastenmüller W, Drexler I, Gasteiger G. J Exp Med. 2016 Dec 12;213(13):3075-3086. doi: 10.1084/jem.20160888.
-
An essential role for the IL-2 receptor in Treg cell function. Chinen T, Kannan AK, Levine AG, Fan X, Klein U, Zheng Y, Gasteiger G, Feng Y, Fontenot JD, Rudensky AY. Nat Immunol. 2016 Nov;17(11):1322-1333. doi: 10.1038/ni.3540.
-
Parallels and differences between innate and adaptive lymphocytes. Bedoui S, Gebhardt T, Gasteiger G, Kastenmüller W. Nat Immunol. 2016 May;17(5):490-4. doi: 10.1038/ni.3432.
-
Tissue residency of innate lymphoid cells in lymphoid and nonlymphoid organs. Gasteiger G, Fan X, Dikiy S, Lee SY, Rudensky AY. Science. 2015 Nov 20;350(6263):981-5. doi: 10.1126/science.aac9593.
-
A Single miRNA-mRNA Interaction Affects the Immune Response in a Context- and Cell-Type-Specific Manner. Lu LF, Gasteiger G, Yu IS, Chaudhry A, Hsin JP, Lu Y, Bos PD, Lin LL, Zawislak CL, Cho S, Sun JC, Leslie CS, Lin SW, Rudensky AY. Immunity. 2015 Jul 21;43(1):52-64. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.04.022.
-
Interactions between innate and adaptive lymphocytes. Gasteiger G, Rudensky AY. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Sep;14(9):631-9. doi: 10.1038/nri3726.
-
Control of the inheritance of regulatory T cell identity by a cis element in the Foxp3 locus. Feng Y, Arvey A, Chinen T, van der Veeken J, Gasteiger G, Rudensky AY. Cell. 2014 Aug 14;158(4):749-763. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.07.031.
-
Nfil3 is crucial for development of innate lymphoid cells and host protection against intestinal pathogens. Geiger TL, Abt MC, Gasteiger G, Firth MA, O'Connor MH, Geary CD, O'Sullivan TE, van den Brink MR, Pamer EG, Hanash AM, Sun JC. J Exp Med. 2014 Aug 25;211(9):1723-31. doi: 10.1084/jem.20140212.
-
IL-2-dependent tuning of NK cell sensitivity for target cells is controlled by regulatory T cells. Gasteiger G, Hemmers S, Firth MA, Le Floc'h A, Huse M, Sun JC, Rudensky AY. J Exp Med. 2013 Jun 3;210(6):1167-78. doi: 10.1084/jem.20122462.
- IL-2-dependent adaptive control of NK cell homeostasis. Gasteiger G, Hemmers S, Bos PD, Sun JC, Rudensky AY. J Exp Med. 2013 Jun 3;210(6):1179-87. doi: 10.1084/jem.20122571.
Interactive online resource/ Interactive atlas of liver ILC1:https://go.uniwue.de/hobit
Interactive online resource / ILC2 Atlas: http://murine-ilc-atlas.ie-freiburg.mpg.de/
- Mini-Symposium zu viralen Infektionen und Herzmuskelerkrankungen - 07.08.2024
- Angeborene Immunzellen sind lernfähiger als gedacht - 09.01.2024
- ERC Synergy Grant für Immuntherapie bei Lebermetastasen - 26.10.2023
- Hobit macht Immunzellen zu Killern - 30.08.2021
- Immunzellen zu Gast in Geweben - 01.10.2020
DFG Emmy-Noether Programm: Interactions of innate and adaptive lymphocytes
ERC Starting Grant: Tissue-resident Lymphocytes: Development and Function in ‚real-life‘ Contexts
DFG SPP 1937: Priority Programme Innate Lymphoid Cells
Prof. Dr. med. Georg Gasteiger





Dr. Lukas Freund



Miriam Kurzwart

Rebekka Mönius

Thomas Oßner


Iris Ramos

Dr. Martina Spiljar
Sigrun Stulz