Osteoporosis / Osteomalacia / Fibrous Dysplasia and Phosphate Metabolism
FGF23 and sFRP4 in bone healing and regeneration – Serum-Markers in inflammation associated osteoporosis and in fracture healing?
in Cooperation with with the Department of Nuclear Medicine University Würzburg, the Center for Musculoskeletal Surgery Charité Berlin and #Universita La Sapienzia, Rome
Lothar Seefried, Regina Ebert, Birgit Mentrup, Doris Schneider, Susanne Wiesner, Bettina Hafen, Norbert Schuetze, Georg Duda, Paolo Bianco, Franz Jakob
The metabolic pathway of phosphate metabolism and its regulation are not entirely characterized. During recent years some progress could be achieved through the molecular clarification of rare diseases like oncogenic osteomalacia and fibrous Dysplasia. The phosphatonins FGF23 und sFRP4 were described and as such important components of phosphate metabolism were identified. FGF23 can be measured in serum. It is elevated in various bone and joint diseases like arthritis and renal osteopathy and it substantially contributes to pathology in fibrous dysplasia. Both FGF23 and sFRP4 inhibit renal 1alpha-hydroxylase and thus cause osteomalacia. Osteoblast precursors secrete the FGF23 polypeptide, inactivation is achieved via partial proteolysis. Inheritable loss-of-function and gain-of-function mutations of FGF23 cause renal phosphate wasting and familial tumoral calcinosis respectively. We find elevated FGF23-levels during bone healing. This indicates a role of FGF23 in bone healing within a certain window of time. Our objections are to further characterize the physiology and pathophysiology of the protein and to evaluate if a subgroup of osteoporosis patients – with special respect to inflammation associated osteoporosis – displays alterations in phosphate metabolism. Our clinical studies are closely related to the experimental projects.
Literature
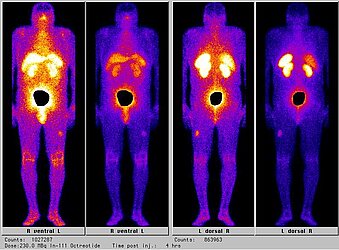
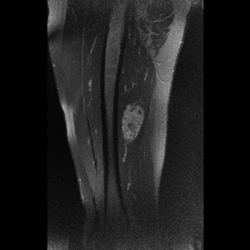
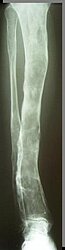
- Lapa C, Genest F, Buck AK, Herrmann K, Kenn W, Rudert M, Jakob F, Seefried L. Diagnostic findings and treatment in a 51-year-old woman with oncogenic osteomalacia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Feb;99(2):385-6. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-3980. Epub 2013 Dec 11.
- Klotz B, Mentrup B, Regensburger M, Zeck S, Schneidereit J, Schupp N, Linden C, Merz C, Ebert R, Jakob F. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 treatment delays cellular aging in human mesenchymal stem cells while maintaining their multipotent capacity. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29959. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029959. Epub 2012 Jan 5.
- Lienau J, Schmidt-Bleek K, Peters A, Haschke F, Duda GN, Perka C, Bail HJ, Schütze N, Jakob F, Schell H. Differential regulation of blood vessel formation between standard and delayed bone healing. J Orthop Res. 2009 Sep;27(9):1133-40. doi: 10.1002/jor.20870.
- Goebel S, Lienau J, Rammoser U, Seefried L, Wintgens KF, Seufert J, Duda G, Jakob F, Ebert R. FGF23 is a putative marker for bone healing and regeneration. J Orthop Res. 2009 Sep;27(9):1141-6. doi: 10.1002/jor.20857.
- Ebert R, Schütze N, Adamski J, Jakob F. Vitamin D signaling is modulated on multiple levels in health and disease. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2006 Mar 27;248(1-2):149-59. Epub 2006 Jan 9. Review.
- Ebert R, Jovanovic M, Ulmer M, Schneider D, Meissner-Weigl J, Adamski J, Jakob F. Down-regulation by nuclear factor kappaB of human 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 1alpha-hydroxylase promoter. Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Oct;18(10):2440-50. Epub 2004 Jul 8.
- Seufert J, Ebert K, Müller J, Eulert J, Hendrich C, Werner E, Schuetze N, Schulz G, Kenn W, Richtmann H, Palitzsch KD, Jakob F. Octreotide therapy for tumor-induced osteomalacia. N Engl J Med. 2001 Dec 27;345(26):1883-8.